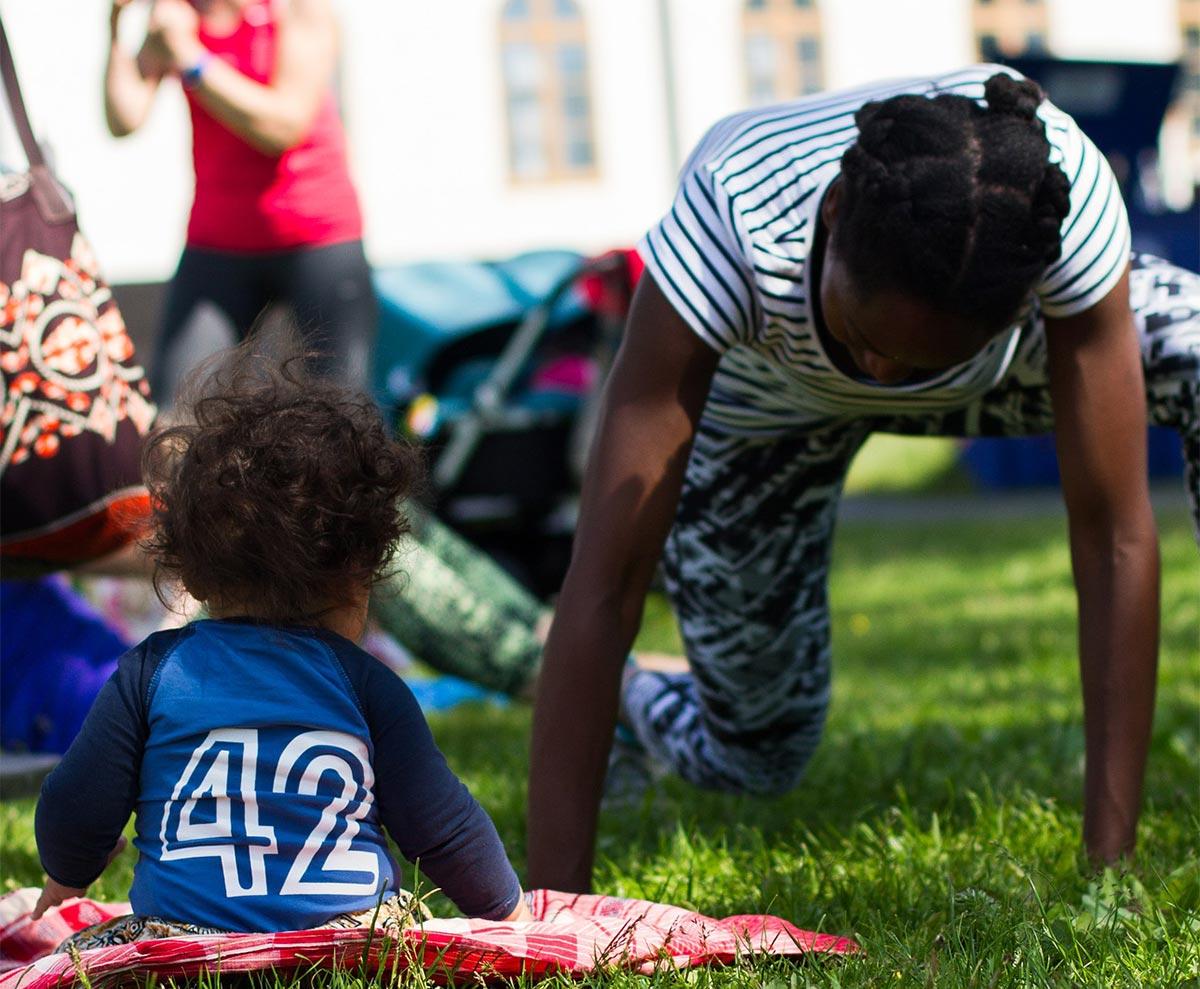In today's digital age, it's easy to assume that young children are constantly active, especially given the boundless energy they often display. However, recent studies reveal a different story: children are sedentary between 73% and 84% of their waking hours. This high level of inactivity is concerning, particularly when coupled with the increasing prevalence of screen time among young children. Excessive screen exposure has been linked to various developmental issues, both physically and socially. It's crucial for parents and caregivers to understand the importance of promoting physical activity and limiting sedentary behaviors to foster healthy growth and development.
Physical Activity Recommendations
The Canadian Society for Exercise Physiology (CSEP) and ParticipACTION have released Canada's first physical activity guidelines for the early years, emphasizing that children aged four and under should be moving more and sitting less throughout the day. These guidelines are supported by research from the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute and the Healthy Active Living and Obesity Research Group (CHEO-HALO).
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), children under five years of age should spend at least 180 minutes in a variety of physical activities at any intensity, spread throughout the day. For children aged three to four years, this should include at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity. Additionally, sedentary screen time should be no more than one hour; less is better. For infants under one year, screen time is not recommended.
The Risks of Excessive Screen Time
While promoting physical activity is essential, it's equally important to address the issue of screen time and sedentary behaviors. Sedentary behaviors are those that involve little physical movement and low energy expenditure, such as sitting or reclining for extended periods. Common sedentary activities for children include using computers, tablets, smartphones, playing video games, watching television or movies, and sitting in strollers or high chairs.
Recent research has highlighted the potential negative impacts of excessive screen time on young children's development. A study published in JAMA Pediatrics found that 1-year-old infants with longer screen time had a higher risk of developmental delays in communication and problem-solving at ages 2 and 4. Another study indicated that increased screen time is associated with behavioral issues and poor vocabulary in children aged 2 to 5 years.
Encouraging Movement and Play
To mitigate these risks, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children aged 2 to 5 years should have no more than one hour of screen time per day, and for children under 18 months, screen time should be limited to video chatting only. They also emphasize the importance of ensuring that any media content is high-quality and that parents co-view media with their children to help them understand what they are seeing and apply it to the world around them.
In addition to limiting screen time, it's beneficial to encourage activities that promote physical movement and social interaction. Simple actions like going for a family walk, playing in the park, or engaging in interactive games can significantly contribute to a child's physical and mental development. These activities not only help in reducing sedentary time but also strengthen the parent-child bond and provide opportunities for learning and exploration.
The Role of Parents
It's also worth noting that parents' screen time can impact their children's screen habits. A study published in BMC Public Health found that there is a strong association between parents' screen time and that of their children, raising concerns that increasing media presence is displacing quality parent-child interactions. Therefore, parents should be mindful of their own screen use and model healthy behaviors for their children.
In conclusion, fostering an active lifestyle and minimizing sedentary behaviors in young children are crucial steps toward ensuring their healthy development. By encouraging regular physical activity, limiting screen time, and engaging in interactive play, parents and caregivers can help children build a strong foundation for a healthy future. Remember, the goal is to "Play More, Sit Less" to promote overall well-being and development in our youngest generation.